The Ultimate Guide to Coaxial Cable: Everything You Need to Know 2024
Coaxial cable has become an essential part of modern communications, powering everything from your internet connection to television signals. This durable, efficient cable technology has stood the test of time, evolving alongside technological advancements. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore coaxial cable in detail, including its history, functionality, types, and applications, to ensure you have all the insights you need.
Introduction to Coaxial Cable
What is Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cable, often shortened to “coax,” is an electrical cable designed to transmit radio frequency (RF) signals efficiently. It consists of a central conductor, surrounded by a layer of insulation, an outer conductor, and a protective jacket. The design minimizes signal loss and interference, making it ideal for data, video, and voice transmissions.
Whether you’re watching cable TV, using broadband internet, or even connecting to a satellite dish, chances are, coaxial cable is working behind the scenes to keep you connected.
Why Coaxial Cable is Important
The importance of coaxial cable lies in its versatility and reliability. It’s one of the oldest forms of cable transmission technology, yet it remains relevant in a world dominated by fiber optics and wireless systems. Its cost-effectiveness, combined with its ability to transmit high-quality signals over considerable distances, ensures it continues to play a pivotal role in telecommunications and broadcasting.
History of Coaxial Cable
The Origin and Development
Coaxial cable was first invented in the 1880s by Oliver Heaviside, a British engineer. It wasn’t until the mid-20th century, however, that coaxial technology saw widespread adoption. Early versions were bulky and limited in range, but they paved the way for innovations that brought about the high-performance cables we use today.
Evolution in Telecommunications
The introduction of coaxial cable revolutionized telecommunications. In the 1940s, it was used to connect long-distance telephone networks. By the 1950s and 60s, it became the backbone of cable television networks, providing a reliable medium for delivering high-quality video signals.
Impact on Modern Technology
Today, coaxial cable has adapted to modern demands, including internet connections and high-definition broadcasts. Despite competition from fiber optics, coaxial cable remains relevant due to its affordability and ease of use.
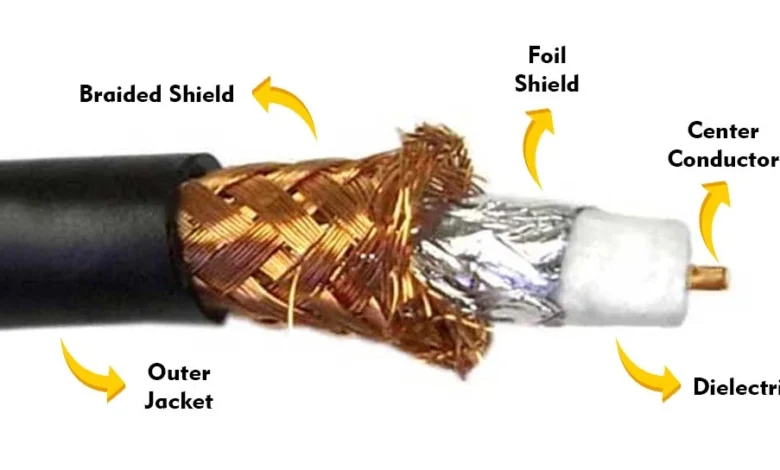
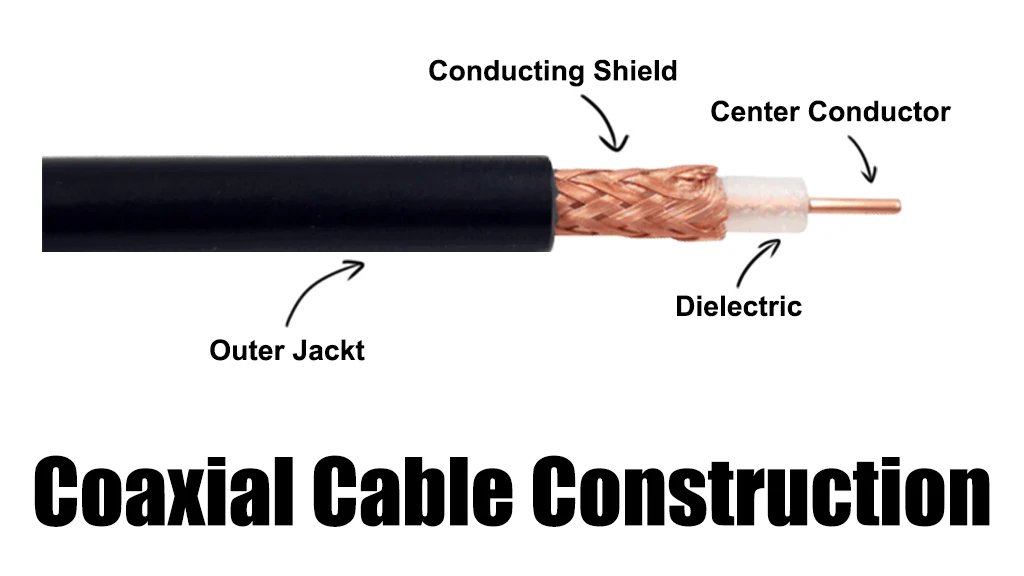
Structure of Coaxial Cable
Inner Conductor
At the heart of every coaxial cable lies the inner conductor. Typically made of copper or copper-coated steel, this component carries the electrical signal. Its quality directly impacts the cable’s performance and signal transmission capabilities.
Dielectric Insulation
Surrounding the inner conductor is a layer of dielectric insulation. This material, often made of polyethylene, ensures minimal signal loss by keeping the conductor electrically isolated.
Outer Shielding and Jacket
The outer shielding, composed of a metal braid or foil, prevents electromagnetic interference (EMI) from disrupting the signal. Finally, the protective jacket shields the cable from physical damage and environmental factors.
Types of Coaxial Cable
RG-6 and RG-11: Differences and Uses

RG-6 and RG-11 are the most common types of coaxial cable used today. RG-6 is ideal for home installations, while RG-11, with its thicker insulation and lower signal loss, is better suited for long-distance applications.
Hardline Coaxial Cable
Hardline coaxial cables are used in commercial and industrial settings. Their robust design and superior shielding make them ideal for transmitting high-power signals.
Triaxial Cable
Triaxial cable, or “Triax,” features an additional layer of shielding, offering improved protection against interference. It’s often used in professional video production and other high-precision applications.
How Coaxial Cable Works
The Role of Conductors
The central conductor carries the signal, while the outer conductor acts as a ground and a shield. Together, they create a consistent transmission path, reducing distortion and loss.
Signal Transmission Mechanism
The coaxial cable transmits signals via electromagnetic waves that travel through the dielectric insulation. This setup ensures minimal interference and high signal fidelity.
Bandwidth Capabilities
Coaxial cable can support a wide range of frequencies, making it suitable for everything from analog video to high-speed internet connections.
Applications of Coaxial Cable
Home Entertainment Systems
From cable TV to streaming devices, coaxial cable is the backbone of most home entertainment systems. Its ability to carry high-definition signals ensures a seamless viewing experience.
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, coaxial cable is used for everything from telephone lines to internet connections. It’s particularly valuable in rural areas where fiber optics may not be cost-effective.
Military and Industrial Applications
Coaxial cable’s durability and reliability make it indispensable in military and industrial applications, where secure and stable communication is paramount.
Advantages of Coaxial Cable
High Signal Quality
Coaxial cable offers excellent signal quality, even over long distances, thanks to its robust shielding and low-loss design.
Durability and Longevity
Built to withstand environmental challenges, coaxial cable is a long-lasting solution for various applications.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to alternatives like fiber optics, coaxial cable is affordable without compromising on performance for most everyday uses.



